Extended Abstract
1. Introduction
oron supplement is one of the microorganisms approved by the US Food and Drug Administration and plays an important role in people’s health. Boric acid and calcium fructoborate are two boron-containing compounds. The main form of boron in body tissues is boric acid and the rest is found in the form of borate anion. Considering the regulation of plasma boron levels through renal excretion, toxicity caused by boron consumption in humans is rare and usually has no adverse effects on humans. People usually consume boron via drinking water and food intake. The daily intake of boron is about 1-3 mg/day for most adults.
The maximum recommended dose for pregnant and lactating women aged over 19 years and all adults is 20 mg/day. The major sources of this ingredient are nuts, dried fruits, grains, fresh vegetables, and fruits. Boron has a positive effect on the growth of bone and central nervous system, hormone regulation, reducing the risk of some types of cancer, improvement of arthritis and associated heart disease symptoms, speeding up the wound healing, pain reduction in gynecological diseases, and kidney stones through reduction of cytokines. Studies show that dietary regimes with low boron intake are common and this deficiency leads to problems in public health and increasing the risk of cancer. In this systematic review, we aimed to investigate the effect of boron supplementation on the prevention and treatment of diseases.
2. Materials and Methods
In this review study, we review all studies related to the preventive and therapeutic effects of boron supplementation published until July 2019 and indexed in Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar, SID, IranMedex, and MagIran databases. For the search, the keywords of “boron supplementation”, “boric acid”, “calcium fructoborate”, “treatment”, and “prevention” were used. Those studies which were related to effectiveness of boron supplementation in the medical field and had a score of 3 or more based on the Jadad Scale were included in the study. Based on initial evaluation, 437 articles were found. of these, 66 papers and 7 books were reviewed. Of 66 papers, only one was in Persian and the rest were in English (Figure 1).
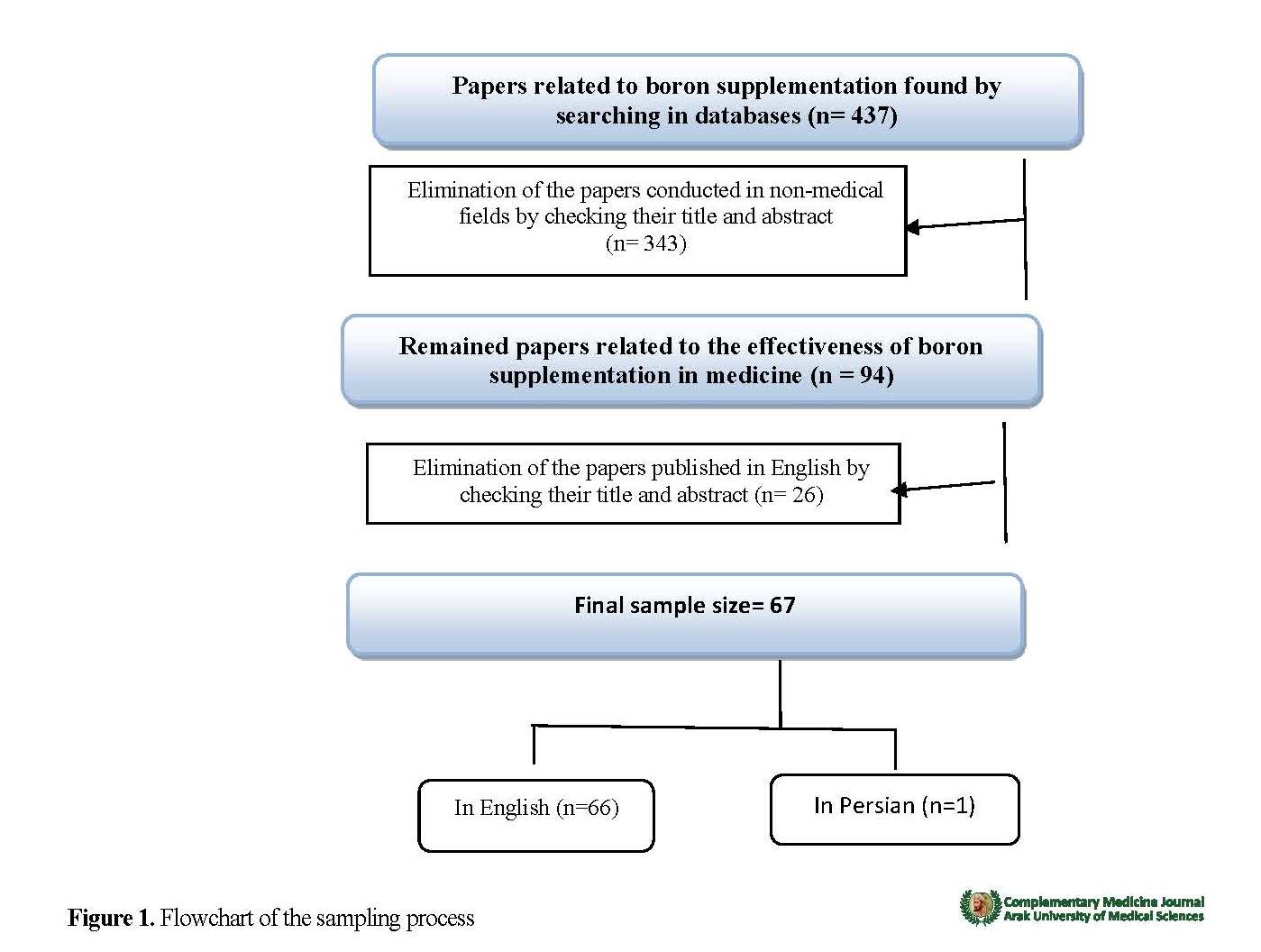
3. Findings
Boron deficiency is harmful to the human body, leading to problems in public health and an increased risk of cancer and even death. The most common symptoms of boron deficiency are arthritis, amnesia, osteoporosis, degenerative and soft cartilage diseases, hormonal disorders, and decreased libido. Studies have shown that the boron intake of less than 1 mg per day creates a context for some problems in the human body and prevents from its benefits to the body.
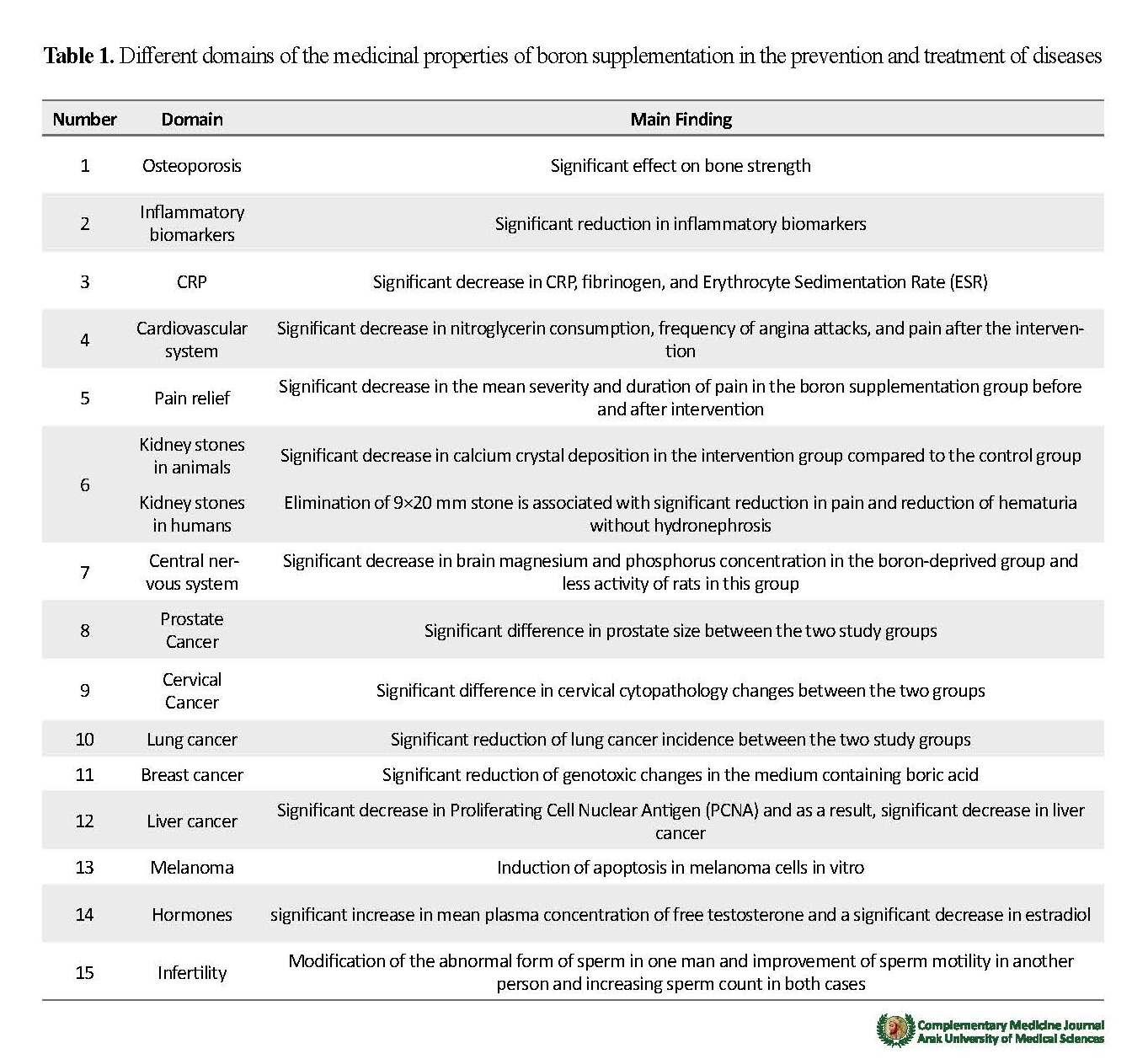
In this study, of 67 reviewed articles, 15 were related to the preventive and therapeutic effects of boron including its effect on osteogenesis, inflammatory response, C-Reactive Protein (CRP), cardiovascular system, pain relief, kidney stone, central nervous system, prostate cancer, cervical cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, liver cancer, melanoma, hormones, and infertility (Table 1). The use of boron in pharmaceuticals is also on the rise.
4. Conclusion
Boron has a positive effect on the growth of bone and central nervous system, hormone regulation, reducing the risk of some types of cancer, improvement of arthritis and associated heart disease symptoms, speeding up the wound healing, pain reduction in gynecological diseases, and kidney stones. Despite the need for boron intake of 1-3 mg per day in adults, symptoms of boron deficiency such as arthritis, amnesia, osteoporosis, degenerative and soft cartilage diseases, hormonal disorders, and decreased libido are still common, and this deficiency can have many adverse effects that can be prevented. Therefore, its consumption as a reasonable dietary and a suitable alternative for common chemical drugs is recommended.
Ethical Considerations
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Authors' contributions
Conceptualization, investigation, analysis and resources, writing-review & editing by all authors; initial draft preparation, visualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition: Somaye Nikkhah.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Dr. Nielsen and Dr. Hunt for their valuable cooperation.
