Introduction
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of death in men worldwide. According to the statistics in 2012, it had the highest prevalence (28%) among the known cancers, and was the second cause of death (11%) after lung cancer (29%). The main problem in prostate cancer treatment currently is the lack of sensitive and specific biomarkers, but according to the role and function of microRNAs, one of the biomarkers in cancer diagnosis and treatment is miR-21. The miR-21 and miR-155 are known as two oncogenic protein activators. The miR-155 dysregulation has been reported in many malignant tumors including leukemia, breast and lung cancers. Recent studies have shown that miR-155 can be significantly expressed in prostate cancer cells.
Studies on the effect of physical activity on prostate cancer have shown different results. Physical activity and exercise can play a significant role in accelerating recovery and delaying its development. Considering that so far no study has been conducted in this field in Iran and other countries, this study aims to assess the effect of eight weeks of aerobic exercise and consumption of pomegranate juice on some miR-155, miR-21 and P53 in men with prostate cancer.
Methods
This is a quasi-experimental study with a pre-test/post-test design. Participants were men with prostate cancer referred to treatment centers in 2020-2021 who were randomly divided into four groups of control, exercise, exercise + supplementation, and supplementation (
Figure 1)
.jpg)
The patients in the exercise group participated in the aerobic exercise program for eight weeks, three sessions per week, each for 60-90 minutes. Each session of the aerobic exercise program was performed in three parts including warm-up, main activity, and cool-down. The warm-up was for 10-15 minutes and included stretching and softening movements, and then the participants performed the main activity for 35-65 minutes on a stationary bike with an intensity of 50-70% of the maximum heart rate. At the end of each session, there was a 10-min stretching and softening movements for cooling down. During this period, no exercises were performed by the control group. The patients in the supplementation and exercise+supplementation groups received 100 cc of natural pomegranate juice one day in the evenings after exercises.
 Results
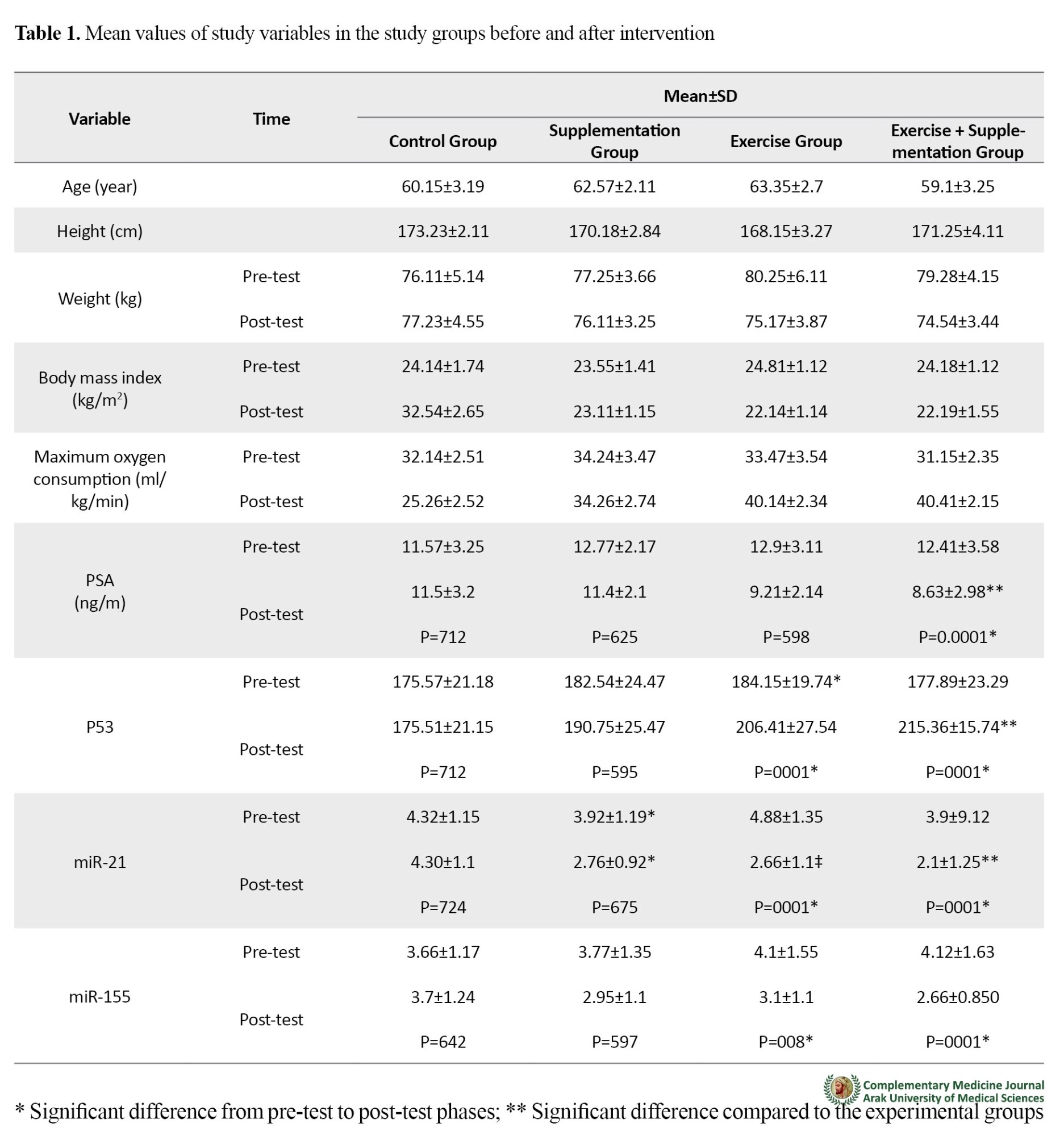
Results
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to check the normal distribution of the data, and Levene's test was used to check the equality of variances. Considering the significance of the tests, dependent t-test and analysis of variance (ANOVA) along with LSD post hoc test were used to examine the differences between groups. A P<0.05 was statistically significant.
Discussion
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of eight weeks of aerobic training and consumption of pomegranate juice on some Micro RNAs and tumor suppressor proteins in men with prostate cancer. The results showed that eight weeks of aerobic exercise combined with consumption of pomegranate juice caused a significant increase in the level of tumor suppressor protein P53. The type and severity of cellular stress may control p53 function by acting on the surface or the activity of p53 protein inducing it. This suggests that proteins that regulate the expression of apoptotic genes associate p53 binding with lower affinity for targets of cell cycle arrest. The P53 plays an important role in metabolism, and since most cancer cells depend on anaerobic glycolysis for energy, the increase in p53 protein due to aerobic exercise can lead to a decrease in anaerobic glycolysis and interrupt the tumor growth.
Eight weeks of aerobic exercise combined with consumption of pomegranate juice and 8 weeks of pomegranate juice consumption alone caused a significant decrease in miR-21 in men with prostate cancer, where the reduction was higher in the group received combined intervention. The miR-21 is considered to be a common oncomiR that limits the activity of signaling pathways such as AKT and MAPK by inhibiting the expression of phosphatases.
Eight weeks of aerobic exercise combined with consumption of pomegranate juice and 8 weeks of pomegranate juice consumption alone caused a significant decrease in miR-155 in men with prostate cancer, where the reduction was higher in the group received combined intervention. The effect of this microRNA is exerted through the reduction of the FOXO3a transcription factor. Aberrant expression of miR-155 increases the survival of cancer cells and increases the resistance of these cells to chemotherapy. Reduction in miR-155 expression can improve cell sensitivity to chemotherapy and promote apoptosis. This suggests a possible functional link between inflammation and cancer by miR-155. Moreover, it has been reported that caspase-3, which is a strong suppressor of apoptosis, is another target of miR-155; in this way, it can also contribute to the occurrence of cancer.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This article is taken from the research plan approved by Qom University, No. 99/14973/D. And its protocols have been approved by the code of ethics IR.GOM.IEC.1398.021 issued by the Ethics Committee of Qom University.
Funding
This study was supported by Qom University.
Authors' contributions
All authors equally contributed to preparing this article.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors of this article thank Qom University and all the participants.
References
- Rawla P. Epidemiology of prostate cancer. World Journal of Oncology. 2019; 10(2):63. [DOI:10.14740/wjon1191] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Dfghjk F, Dfghj D, Dfghjk D. [The effect of 10 weeks of high-intensity exercise training on resting levels of some angiogenesis and pulmonary function of men with prostate cancer (Persian)]. Journal of Fasa University of Medical Sciences. 2019; 8(4):1097-105. [Link]
- AsghariRakabdarkolaee M, Barari A, Abdi A, Hasrak K. [The effect of eight-week concurrent training on aerobic capacity and serum level of p53 tumor suppressor protein in prostate cancer patients: A clinical trial (Persian)]. Journal of Rafsanjan University of Medical Sciences. 2018; 17(8):731-44. [Link]
- Filella X, Foj L. miRNAs as novel biomarkers in the management of prostate cancer. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM). 2017; 55(5):715-36. [DOI:10.1515/cclm-2015-1073] [PMID]
- Bidarra D, Constâncio V, Barros-Silva D, Ramalho-Carvalho J, Moreira-Barbosa C, Antunes L, et al. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for prostate cancer detection and metastasis development prediction. Frontiers in oncology. 2019; 9:900. [DOI:10.3389/fonc.2019.00900] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Shadmanfard A, Nemati A, Naghizadeh Baghi A, Mazani M. The effect of pomegranate juice supplementation on oxidative stress in young healthy males. Journal of Ardabil University of Medical Sciences. 2012; 12(5):77-86. [Link]
- Zarban A, Malekaneh M, Reza Boghrati M. Antioxidant properties of pomegranate juice and its scavenging effect on free radicals. Journal of Birjand University of Medical Sciences. 2007; 14(3):9-15. http://journal.bums.ac.ir/article-1-149-en.html
- Akbarpour M, Fathollahi Shoorabeh F, Mardani M, Amini Majd F. [Effects of eight weeks of resistance training and consumption of pomegranate on GLP-1, DPP-4 and glycemic statuses in women with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial (Persian)]. Nutrition and Food Sciences Research. 2021; 8(1):5-10. [Link]
- Akbarpour M, Fathollahi SF, Faraji F. Effect of eight weeks of resistance training with supplementation of pomegranate juice on oxidative/antioxidant factors and lipid profiles in women with type 2 diabetes. Knowledge and Health. 2019; 14(3):52-8. [Link]
- Song CJ, Chen H, Chen LZ, Ru GM, Guo JJ, Ding QN. The potential of microRNAs as human prostate cancer biomarkers: a meta-analysis of related studies. Journal of cellular biochemistry. 2018; 119(3):2763-86. [DOI:10.1002/jcb.26445] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Badr FM. Potential role of miR-21 in breast cancer diagnosis and therapy. SciMed Central. 2016; 3(5):1068-75. [Link]
- Feng YH, Tsao CJ. Emerging role of microRNA-21 in cancer. Biomedical reports. 2016; 5(4):395-402. [DOI:10.3892/br.2016.747] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Wang F, Zheng Z, Guo J, Ding X. Correlation and quantitation of microRNA aberrant expression in tissues and sera from patients with breast tumor. Gynecologic oncology. 2010; 119(3):586-93. [DOI:10.1016/j.ygyno.2010.07.021] [PMID]
- Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Mo YY. MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2007; 282(19):14328-36. [DOI:10.1074/jbc.M611393200] [PMID]
- Le Quesne J, Caldas C. Micro-RNAs and breast cancer. Molecular oncology. 2010; 4(3):230-41. [DOI:10.1016/j.molonc.2010.04.009] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Shoorabeh FF, Dabidiroshan V, Saraf BS, Nuri R. Investigating the effects of regular resistance training and prostatic massage on proinflammatory markers and serum prostate-specific antigen levels in males with prostate cancer. Middle East Journal of Rehabilitation and Health. 2016; 3(1). [DOI:10.17795/mejrh-33651]
- Wang PY, Zhuang J, Hwang PM. p53: exercise capacity and metabolism. Current opinion in oncology. 2012; 24(1):76-82. [DOI:10.1097/CCO.0b013e32834de1d8] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Lago CU, Sung HJ, Ma W, Wang PY, Hwang PM. p53, aerobic metabolism, and cancer. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 2011; 15(6):1739-48. [DOI:10.1089/ars.2010.3650] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Saed-Mocheshi S, Saghebjoo M, Vahabzadeh Z, Sheikholeslami Vatani D. The effect of eight weeks aerobic training and green tea extract on some inflammatory factors in prostate tissue of healthy rats. Journal of Sabzevar University of Medical Sciences. 2020; 27(3):394-401. [Link]
- Tamura RE, da Silva Soares RB, Costanzi-Strauss E, Strauss BE. Autoregulated expression of p53 from an adenoviral vector confers superior tumor inhibition in a model of prostate carcinoma gene therapy. Cancer biology & therapy. 2016; 17(12):1221-30. [Link]
- Nelson ME, Rejeski WJ, Blair SN, Duncan PW, Judge JO, King AC, et al. Physical activity and public health in older adults: recommendation from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2007; 116(9):1094. [DOI:10.1249/mss.0b013e3180616aa2] [PMID]
- Feng Z, Levine AJ. The regulation of energy metabolism and the IGF-1/mTOR pathways by the p53 protein. Trends in Cell Biology. 2010; 20(7):427-34. [DOI:10.1016/j.tcb.2010.03.004] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Bouvet M, Ellis LM, Nishizaki M, Fujiwara T, Liu W, Bucana CD, Fang B, Lee JJ, Roth JA. Adenovirus-mediated wild-type p53 gene transfer down-regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression and inhibits angiogenesis in human colon cancer. Cancer research. 1998; 58(11):2288-92. [Link]
- Qi J, Wang J, Katayama H, Sen S, Liu SM. Circulating microRNAs (cmiRNAs) as novel potential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasma. 2013; 60(2):135-42. [DOI:10.4149/neo_2013_018] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Wang W, Luo YP. MicroRNAs in breast cancer: oncogene and tumor suppressors with clinical potential. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B. 2015; 16(1):18-31. [DOI:10.1631/jzus.B1400184] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Cai ZK, Chen Q, Chen YB, Gu M, Zheng DC, Zhou J, Wang Z. microRNA‑155 promotes the proliferation of prostate cancer cells by targeting annexin 7. Molecular Medicine Reports. 2015; 11(1):533-8. [DOI:10.3892/mmr.2014.2744] [PMID]
- Basu S, Majumder S, Bhowal A, Ghosh A, Naskar S, Nandy S, et al. A study of molecular signals deregulating mismatch repair genes in prostate cancer compared to benign prostatic hyperplasia. PloS one. 2015; 10(5):e0125560. [DOI:10.1371/jouRNAl.pone.0125560] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Rouzbehan B, Ebrahim K, Ghazalian F. The effect of aerobic training and pomegranate juice on serum levels of some microRNAs related to the oxidant/antioxidant system in women recovering from breast cancer. Yafteh. 2021; 23(4):133-148. [DOI:10.32592/Yafteh.2021.23.4.11]
.jpg)

